
Lecture 6 January 12 2016 Biotech 3 Lecture
YAC and BAC vectors are two types of artificial vector systems designed to clone large genomic DNA fragments. They have multiple applications in the preparation of genomic and cDNA libraries. Key Areas Covered 1. What are YAC Vectors - Definition, Features, Construction 2. What are BAC Vectors - Definition, Features, Applications 3.

Types of vectors for engineering Plasmids, Phagemids, Cosmids, BAC, YAC and PAC YouTube
A bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) is an engineered DNA molecule used to clone DNA sequences in bacterial cells (for example, E. coli). BACs are often used in connection with DNA sequencing. Segments of an organism's DNA, ranging from 100,000 to about 300,000 base pairs, can be inserted into BACs.

Cosmid Vectors, YAC and BAC Expression Vectors
The procedure includes the preparation of BIBAC vectors, the preparation of clonable fragments of the desired size from the source DNA, the construction and transformation of BIBACs and, finally,.

Difference Between YAC and BAC Vectors YAC vs BAC Vectors
Yeast artificial chromosomes or yac vector - This lecture explains about the yeast artificial chromosomes also know and the yac vector and the use of yeast a.

Difference Between BAC and YAC Gene Cloning Vectors Biologyexams4u YouTube
Both the BAC map and the YAC map have been anchored to version 3.1 of the rat genome sequence assembly using end sequences for fingerprinted BAC clones. The anchored BAC clones provide an ordered, high-resolution, redundant clone set spanning the sequence assembly, providing the research community with easy identification and access to BAC.

10 Differences between BAC and YAC Vector Major Differences
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae [1], which is then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. By inserting large fragments of DNA, from 100-1000 kb, the inserted sequences can be cloned and physically mapped using a process called chromosome walking.

Retrofitting of a circular YAC into a BAC containing the Neo R... Download Scientific Diagram
Difference between YAC and BAC Vectors A vector is a stretch of DNA that acts as a transport for carrying foreign genetic material into host cells, where it can replicate and express itself. The four types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids and artificial chromosomes. Vectors are constructed for different purposes.

Schematic representation of retrofitting a circular YAC into a BAC... Download Scientific Diagram
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) have become essential research tools as they enable large fragments of DNA to be cloned. In order to overcome several disadvantages of YACs, including chimaerism and instability, several complementary bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) vectors have been develop.

HAC assembling via bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC)/yeast... Download Scientific Diagram
6 Minute video Explaining Bacterial Artificial Chromosome vs Yeast Artificial Chromosome 5 Differences between YAC and BAC0:00 Introduction 0:15 Difference N.

Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) What is the purpose of using BAC and YAC vectors? YouTube
Two types of vectors commonly used in cloning are yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) and bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs). While both serve similar purposes, there are distinct differences between them. Advertisements
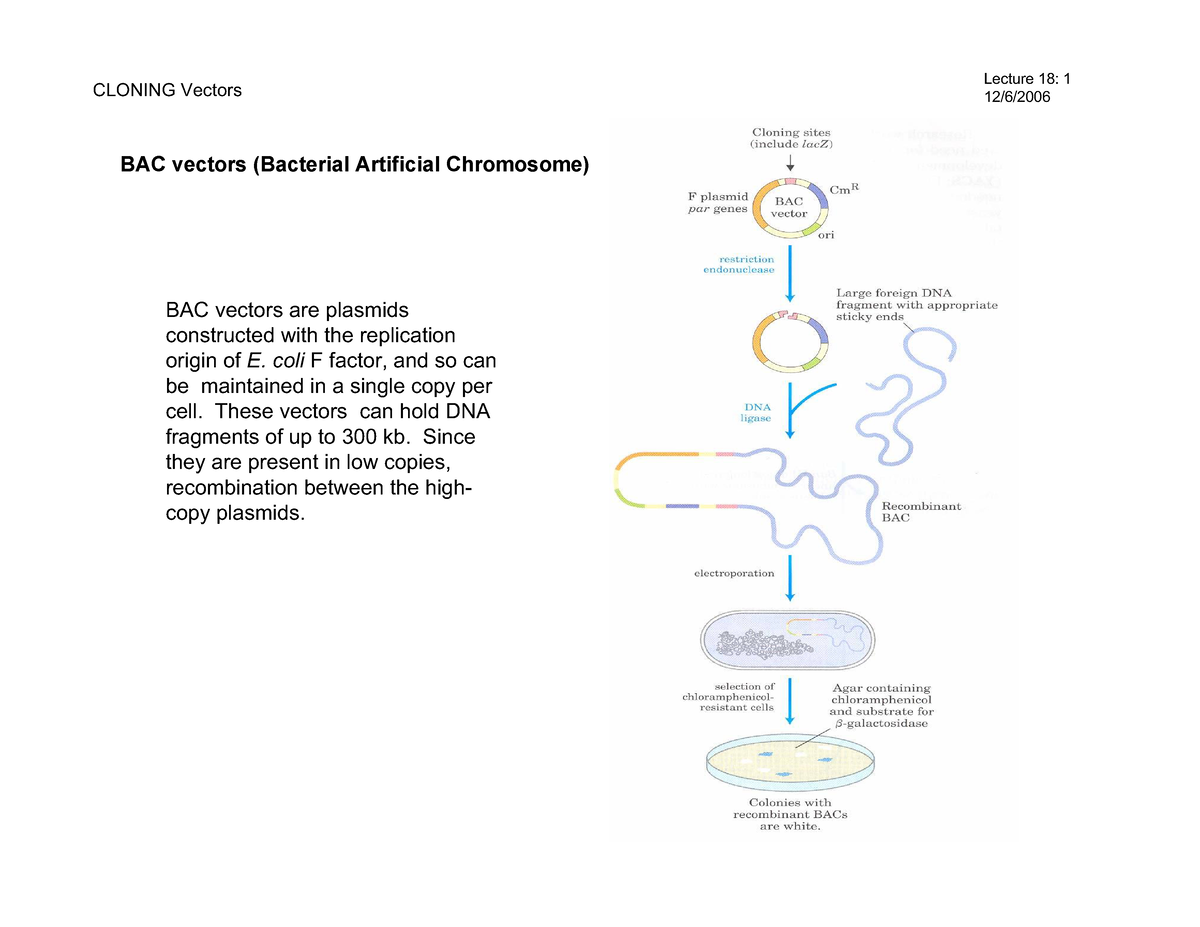
Different types of cloning vectors (BAC and YAC). CLONING Vectors Lecture 18 112/6/ BAC
These BAC clones provide ∼13-fold redundant coverage of the genome and have been assembled into 376 fingerprint contigs. A yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) map was also constructed and aligned with the BAC map via fingerprinted BAC and P1 artificial chromosome clones (PACs) sharing interspersed repetitive sequence markers with the YAC-based.
Bacteriophage Vectors Cosmid BAC YAC Phagmid Animal and Plant Vectors
Artificial chromosomes have now become a major research tool in both genome analysis and in the functional characterization of genes. Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) (R.ef. 1; see Glossary) have led the way in mapping complex genomes, and large YAC contigs (contiguous sets of overlapping clones) now cover much of the human genome2. YACs.

Cosmid Vectors, YAC and BAC Expression Vectors
YAC (Yeast Artificial Chromosome) and BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) vectors are two types of cloning vectors used in molecular biology and genetics research to manipulate and study large DNA fragments, including entire genes or even entire chromosomes.

Bac and Yac Boris Gibson
YAC and BAC vectors are two genetically engineered artificial vectors designed to clone large DNA fragments. Now both these vectors are very much modified based on requirements. Let's differentiate the basic YAC and BAC vector in this post. Difference Between BAC and YAC Gene Cloning Vectors ||Biologyexams4u Watch on

Difference Between YAC and BAC Vectors
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast. It is a human-engineered DNA molecule used to clone DNA sequences in yeast cells. They are the products of a recombinant DNA cloning methodology to isolate and propagate very large segments of DNA in a yeast host.

Yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) What are the components of yeast artificial chromosome
Diagram of the TAR cloning vector pJYB. The vector contains BAC and YAC (bacterial and yeast artificial chromosomes, respectively), and polylinker cassettes. A YAC cassette contains a yeast centromere (CEN6) and a yeast selectable marker, HIS3. A BAC cassette contains the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CM R) gene and the F′-origin of.